

The sreg package for R, offers a toolkit
for estimating average treatment effects (ATEs) in stratified randomized
experiments. It supports a wide range of stratification designs,
including matched pairs, \(k\)-tuple
designs, and larger strata with many units — possibly of unequal size
across strata. The package is designed to accommodate scenarios with
multiple treatments, and cluster-level treatment assignments, and
accomodates optimal linear covariate adjustment based on baseline
observable characteristics. The package computes estimators and standard
errors based on Bugni, Canay, Shaikh (2018); Bugni, Canay, Shaikh,
Tabord-Meehan (2023); Jiang, Linton, Tang, Zhang (2023); Bai, Jiang,
Romano, Shaikh, Zhang (2024); Bai (2022); Bai, Romano, Shaikh (2022);
Liu (2024); and Cytrynbaum (2024).
Dependencies: dplyr,
tidyr, extraDistr, rlang
Suggests: haven, knitr,
rmarkdown, testthat (>= 3.0.0)
R version required:
>= 2.10
Juri Trifonov jutrifonov@u.northwestern.edu
Yuehao Bai yuehao.bai@usc.edu
Azeem Shaikh amshaikh@uchicago.edu
Max Tabord-Meehan m.tabordmeehan@utoronto.ca
PDF version of the manual: Download PDF
Big Strata: Sketch of the derivation of the ATE variance estimator under cluster-level treatment assignment: Download PDF
Big Strata: Expressions for the multiple treatment case (with and without clusters): Download PDF
Small Strata: Expressions for the multiple treatment case (with and without clusters): Download PDF
Mixed Design: Expressions for the multiple treatment case (with and without clusters): Download PDF
Install the official CRAN release using:
install.packages("sreg")trying URL 'https://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/cran/src/contrib/sreg_1.0.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 43389 bytes (42 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 42 KB
* installing *source* package ‘sreg’ ...
** package ‘sreg’ successfully unpacked and MD5 sums checked
** using staged installation
** R
** data
*** moving datasets to lazyload DB
** inst
** byte-compile and prepare package for lazy loading
** help
*** installing help indices
** building package indices
** installing vignettes
** testing if installed package can be loaded from temporary location
** testing if installed package can be loaded from final location
** testing if installed package keeps a record of temporary installation path
* DONE (sreg)
The downloaded source packages are in
‘/private/var/folders/mp/06gjwr8j56zdp5j2vgdkd4z40000gq/T/RtmpVk96vN/downloaded_packages’library(sreg)#> ____ ____ _____ ____ Stratified Randomized
#> / ___|| _ \| ____/ ___| Experiments
#> \___ \| |_) | _|| | _
#> ___) | _ <| |__| |_| |
#> |____/|_| \_\_____\____| version 1.0.1
#> Type 'citation("sreg")' for citing this R package in publications. The latest development version can be installed using
devtools.
library(devtools)
install_github("jutrifonov/sreg")Downloading GitHub repo jutrifonov/sreg@HEAD
── R CMD build ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
✔ checking for file ‘/private/var/folders/mp/06gjwr8j56zdp5j2vgdkd4z40000gq/T/RtmpVk96vN/remotes1026130d7f9b4/jutrifonov-sreg-53c1377/DESCRIPTION’ ...
─ preparing ‘sreg’:
✔ checking DESCRIPTION meta-information ...
─ checking for LF line-endings in source and make files and shell scripts
─ checking for empty or unneeded directories
─ building ‘sreg_2.0.0.9000.tar.gz’
Installing package into ‘/opt/homebrew/lib/R/4.4/site-library’
(as ‘lib’ is unspecified)
* installing *source* package ‘sreg’ ...
** using staged installation
** R
** data
*** moving datasets to lazyload DB
** inst
** byte-compile and prepare package for lazy loading
** help
*** installing help indices
** building package indices
** installing vignettes
** testing if installed package can be loaded from temporary location
** testing if installed package can be loaded from final location
** testing if installed package keeps a record of temporary installation path
* DONE (sreg)library(sreg)ℹ Loading sreg
#> ____ ____ _____ ____ Stratified Randomized
#> / ___|| _ \| ____/ ___| Experiments
#> \___ \| |_) | _|| | _
#> ___) | _ <| |__| |_| |
#> |____/|_| \_\_____\____| version 2.0.0.9000
#> Type 'citation("sreg")' for citing this R package in publications. sreg()Estimates the ATE(s) and the corresponding standard error(s) for a (collection of) treatment(s) relative to a control.
sreg(Y, S = NULL, D, G.id = NULL, Ng = NULL, X = NULL, HC1 = TRUE, small.strata = FALSE)Y - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame/tibble of the observed
outcomes;S - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame/tibble of strata indicators \(\\{0, 1, 2, \ldots\\}\); if
NULL then the estimation is performed assuming no
stratification;D - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame/tibble of treatments indexed by
\(\\{0, 1, 2, \ldots\\}\), where
D = 0 denotes the control;G.id - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame/tibble of cluster indicators; if
NULL then estimation is performed assuming treatment is
assigned at the individual level;Ng - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame/tibble of cluster sizes; if
NULL then Ng is assumed to be equal to the
number of available observations in every cluster;X - a
matrix/data.frame/tibble with columns representing the
covariate values for every observation; if NULL then the
estimator without linear adjustments is applied [^*];HC1 - a TRUE/FALSE
logical argument indicating whether the small sample correction should
be applied to the variance estimator;small.strata - a
TRUE/FALSE logical argument indicating whether the
estimators for small strata (i.e., strata with few units, such as
matched pairs or n-tuples) should be used [^**]. [^*]: Note: sreg
cannot use individual-level covariates for covariate adjustment in
cluster-randomized experiments. Any individual-level covariates will be
aggregated to their cluster-level averages. [^**]: Note: if the
data exhibit a mixed design (i.e., most observations are in small
strata, but some are in big strata) and
small.strata = TRUE, the function implements the mixed
estimator—a weighted average of small and big strata estimators. See the
supplementary PDF for details and expressions.Here we provide an example of a data frame that can be used with
sreg.
| Y | S | D | G.id | Ng | x_1 | x_2 |
|--------------|---|---|------|----|------------|---------------|
| -0.57773576 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 1.5597899 | 0.03023334 |
| 1.69495638 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 1.5597899 | 0.03023334 |
| 2.02033740 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| 1.22020493 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| 1.64466086 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| -0.32365109 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| 2.21008191 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| -2.25064316 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |
| 0.37962312 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 0.8747419 | -0.77090031 |sreg prints a “Stata-style” table containing
the ATE estimates, corresponding standard errors, \(t\)-statistics, \(p\)-values, \(95\)% asymptotic confidence intervals, and
significance indicators for different levels \(\alpha\). The example of the printed output
is provided below.
Saturated Model Estimation Results under CAR
Observations: 2710
Clusters: 100
Number of treatments: 2
Number of strata: 10
Setup: big strata
Standard errors: adjusted (HC1)
Treatment assignment: cluster level
Covariates used in linear adjustments:
---
Coefficients:
Tau As.se T-stat P-value CI.left(95%) CI.right(95%) Significance
1 1.13687 0.31181 3.64608 0.00027 0.52574 1.74799 ***
2 0.66447 0.30263 2.19565 0.02812 0.07133 1.25761 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 `***` 0.001 `**` 0.01 `*` 0.05 `.` 0.1 ` ` 1The function returns an object of class sreg that is a
list containing the following elements:
tau.hat - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of ATE
estimates, where \(|\mathcal A|\)
represents the number of treatments;
se.rob - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of standard
errors estimates, where \(|\mathcal
A|\) represents the number of treatments;
t.stat - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of \(t\)-statistics, where \(|\mathcal A|\) represents the number of
treatments;
p.value - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of
corresponding \(p\)-values, where \(|\mathcal A|\) represents the number of
treatments;
CI.left - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of the left
bounds of the \(95\)% as. confidence
interval;
CI.right - a \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector of the right
bounds of the \(95\)% as. confidence
interval;
data - an original data of the form
data.frame(Y, S, D, G.id, Ng, X);
lin.adj - a data.frame
representing the covariates that were used in implementing linear
adjustments;
small.strata - a
TRUE/FALSE logical argument indicating whether the
estimators for small strata (e.g., matched pairs or n-tuples) were
used;
HC1 - a TRUE/FALSE
logical argument indicating whether the small sample correction (HC1)
was applied to the variance estimator.
Here, we provide the empirical application example using the data
from (Chong et al., 2016), who studied the effect of iron deficiency
anemia on school-age children’s educational attainment and cognitive
ability in Peru. The example replicates the empirical illustration from
(Bugni et al., 2019). For replication purposes, the data is included in
the package and can be accessed by running data("AEJapp").
This example can be accessed directly in R via
help(sreg).
library(sreg, dplyr, haven)The description of the dataset can be accessed using
help():
help(AEJapp)We can upload the AEJapp dataset to the R
session via data():
data("AEJapp")
data <- AEJappIt is pretty straightforward to prepare the data to fit the package
syntax using dplyr:
Y <- data$gradesq34
D <- data$treatment
S <- data$class_level
data.clean <- data.frame(Y, D, S)
data.clean <- data.clean %>%
mutate(D = ifelse(D == 3, 0, D))
Y <- data.clean$Y
D <- data.clean$D
S <- data.clean$S
head(data.clean)
Y D S
1 11.2 1 1
2 12.4 0 3
3 11.9 0 5
4 13.1 0 1
5 13.4 2 2
6 10.7 0 1We can take a look at the frequency table of D and
S:
table(D = data.clean$D, S = data.clean$S)
S
D 1 2 3 4 5
0 15 19 16 12 10
1 16 19 15 10 10
2 17 20 15 11 10Now, it is straightforward to replicate the results from (Bugni et
al, 2019) using sreg:
result <- sreg::sreg(Y = Y, S = S, D = D)
print(result)Saturated Model Estimation Results under CAR
Observations: 215
Number of treatments: 2
Number of strata: 5
Setup: big strata
Standard errors: adjusted (HC1)
Treatment assignment: individual level
Covariates used in linear adjustments:
---
Coefficients:
Tau As.se T-stat P-value CI.left(95%) CI.right(95%) Significance
1 -0.05113 0.20645 -0.24766 0.80440 -0.45577 0.35351
2 0.40903 0.20651 1.98065 0.04763 0.00427 0.81379 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 `***` 0.001 `**` 0.01 `*` 0.05 `.` 0.1 ` ` 1Besides that, sreg allows adding linear adjustments
(covariates) to the estimation procedure:
pills <- data$pills_taken
age <- data$age_months
data.clean <- data.frame(Y, D, S, pills, age)
data.clean <- data.clean %>%
mutate(D = ifelse(D == 3, 0, D))
Y <- data.clean$Y
D <- data.clean$D
S <- data.clean$S
X <- data.frame("pills" = data.clean$pills, "age" = data.clean$age)
result <- sreg::sreg(Y, S, D, G.id = NULL, X = X)
print(result)
Saturated Model Estimation Results under CAR with linear adjustments
Observations: 215
Number of treatments: 2
Number of strata: 5
Setup: big strata
Standard errors: adjusted (HC1)
Treatment assignment: individual level
Covariates used in linear adjustments: pills, age
---
Coefficients:
Tau As.se T-stat P-value CI.left(95%) CI.right(95%) Significance
1 -0.02862 0.17964 -0.15929 0.87344 -0.38071 0.32348
2 0.34609 0.18362 1.88477 0.05946 -0.01381 0.70598 .
---
Signif. codes: 0 `***` 0.001 `**` 0.01 `*` 0.05 `.` 0.1 ` ` 1Beginning with version 2.0.0+, the sreg
package supports experimental designs with small strata (e.g., matched
pairs or k-tuples) via the small.strata argument in the
sreg function. We demonstrate its implementation using simulated data
generated by sreg.rgen() under a matched triplets
design.
data <- sreg.rgen(n = 300, tau.vec = c(1.2, 0.8), cluster = FALSE, small.strata = TRUE, k = 3, treat.sizes = c(1, 1, 1))
> head(data)
Y S D x_1 x_2
1 2.6455170 1 0 5.594675 1.9023835
2 6.6589024 1 2 6.450984 4.2343208
3 4.3412644 1 1 4.787852 3.1895694
4 -0.7592291 2 2 6.240883 0.7458935
5 5.1391241 2 1 6.076305 2.6105942
6 2.3934378 2 0 5.403182 3.4032419result <- sreg(Y = data$Y, S = data$S, D = data$D, X = data.frame('x_1' = data$x_1, 'x_2' = data$x_2), small.strata = TRUE)
> print(result)
Saturated Model Estimation Results under CAR with linear adjustments
Observations: 300
Number of treatments: 2
Number of strata: 100
Setup: small strata
Strata size (k): 3
Standard errors: adjusted (HC1)
Treatment assignment: individual level
Covariates used in linear adjustments: x_1, x_2
---
Coefficients:
Tau As.se T-stat P-value CI.left(95%) CI.right(95%) Significance
1 1.11577 0.13995 7.97258 0e+00 0.84147 1.39006 ***
2 0.58806 0.13439 4.37574 1e-05 0.32466 0.85147 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 `***` 0.001 `**` 0.01 `*` 0.05 `.` 0.1 ` ` 1plot.sreg()Visualizes the estimated average treatment effects (ATEs) and their
confidence intervals from an object returned by sreg().
This function defines an S3 method for the generic
plot() function for objects of class sreg.
plot(x,
treatment_labels = NULL,
title = "Estimated ATEs with Confidence Intervals",
bar_fill = NULL,
point_shape = 23,
point_size = 3,
point_fill = "white",
point_stroke = 1.2,
point_color = "black",
label_color = "black",
label_size = 4,
bg_color = NULL,
grid = TRUE,
zero_line = TRUE,
y_axis_title = NULL,
x_axis_title = NULL,
...)x - an object of class
sreg, returned by the sreg() function;treatment_labels - an optional
vector of labels to display on the y-axis; if
NULL, defaults to “Treatment 1”, “Treatment 2”, etc.;title - an optional
string specifying the plot title; default is “Estimated
ATEs with Confidence Intervals”;bar_fill - an optional color
specification for the confidence interval bars; can be NULL
(default viridis scale), a single color, or a vector of two colors for a
gradient;point_shape - an integer
specifying the shape of the point representing the estimated ATE;
default is 23 (diamond);point_size - a numeric
value specifying the size of the ATE point;point_fill - a string
indicating the fill color of the ATE point shape;point_stroke - a numeric
value for the stroke (border thickness) of the ATE point shape;point_color - a string
specifying the outline color of the ATE point;label_color - a string
indicating the color of the text label displaying the estimate and
standard error;label_size - a numeric
value for the size of the text label;bg_color - an optional
string specifying the background color of the plot panel;
if NULL, the default theme background is used;grid - a TRUE/FALSE
argument indicating whether grid lines should be displayed
(TRUE by default);zero_line - a TRUE/FALSE
argument indicating whether to include a dashed vertical line at 0
(TRUE by default);y_axis_title - an optional
string specifying the y-axis title; if NULL,
no title is displayed;x_axis_title - an optional
string specifying the x-axis title; if NULL,
no title is displayed;... - additional arguments passed to
other methods (not used in this method).Invisibly returns the ggplot object used to generate the
figure. The function is called primarily for its side effect — rendering
the plot. ### Example
library("sreg")
library("dplyr")
library("haven")
data <- sreg.rgen(n = 1000, tau.vec = c(-0.3, 0.2), n.strata = 4, cluster = FALSE)
Y <- data$Y
S <- data$S
D <- data$D
X <- data.frame("x_1" = data$x_1, "x_2" = data$x_2)
result <- sreg(Y, S, D, G.id = NULL, Ng = NULL, X)
plot(result)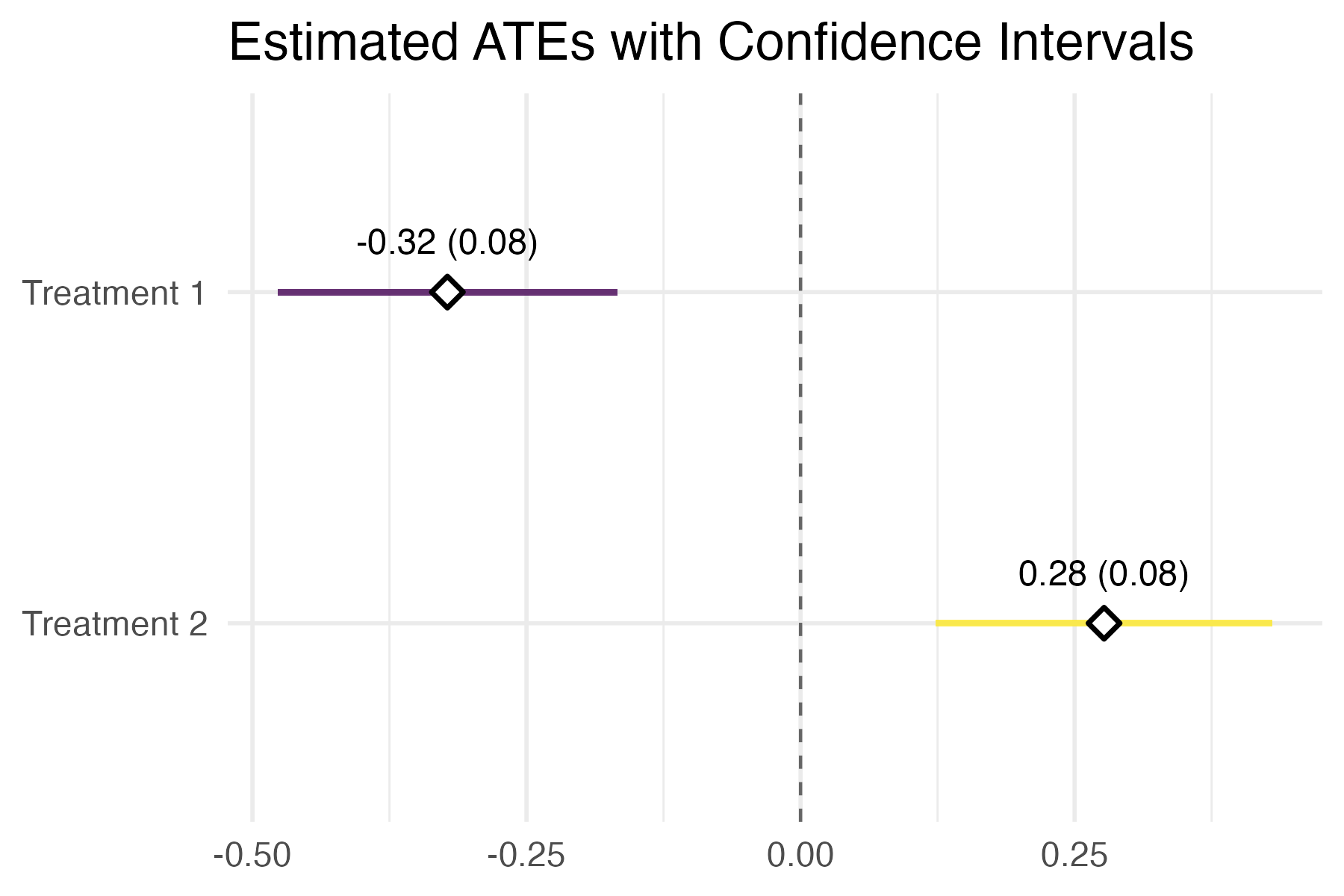
print.sreg()Prints a summary table of the estimated treatment effects from an
object returned by sreg(). This function defines an
S3 method for the generic print() function for
objects of class sreg. This method prints a formatted
summary table that includes the estimated average treatment effects,
standard errors, \(p\)-values,
confidence intervals, and details about the experimental design.
print.sreg(x, ...)x - an object of class
sreg, typically returned by the sreg()
function;... - additional arguments.sreg.rgen()Generates the observed outcomes, treatment assignments, strata indicators, cluster indicators, cluster sizes, and covariates for estimating the treatment effect following the stratified block randomization design under covariate-adaptive randomization (CAR).
sreg.rgen(n, Nmax = 50, n.strata,
tau.vec = c(0), gamma.vec = c(0.4, 0.2, 1),
cluster = TRUE, is.cov = TRUE, small.strata = FALSE,
k = 3, treat.sizes = c(1, 1, 1))n - a total number of observations in
a sample;Nmax - a maximum size of generated
clusters (maximum number of observations in a cluster);n.strata - an integer
specifying the number of strata;tau.vec - a numeric \(1 \times |\mathcal A|\) vector
of treatment effects, where \(|\mathcal
A|\) represents the number of treatments;gamma.vec - a numeric \(1 \times 3\) vector of
parameters corresponding to covariates;cluster - a TRUE/FALSE
argument indicating whether the dgp should use a cluster-level treatment
assignment or individual-level;is.cov - a TRUE/FALSE
argument indicating whether the dgp should include covariates or
not;small.strata - a
TRUE/FALSE argument indicating whether the data-generating
process should use a small-strata design (e.g., matched pairs, \(n\)-tuples);k - an integer specifying the number
of units per stratum when small.strata = TRUE;treat.sizes - a numeric \(1 \times (|\mathcal A| + 1)\)
vector specifying the number of units assigned to each
treatment within a stratum; the first element corresponds to control
units (\(D = 0\)), the second to the
first treatment (\(D = 1\)), and so
on.Y - a numeric \(n \times 1\) vector of the
observed outcomes;S - a numeric \(n \times 1\) vector of strata
indicators;D - a numeric \(n \times 1\) vector of
treatments indexed by \(\\{0, 1, 2,
\ldots\\}\), where D = 0 denotes the control;G.id - a numeric \(n \times 1\) vector of cluster
indicators;Ng - a numeric
vector/matrix/data.frame of cluster sizes; if
NULL then Ng is assumed to be equal to the
number of available observations in every cluster;X - a data.frame with
columns representing the covariate values for every observation.library(sreg)
# big stata
data <- sreg.rgen(n = 1000, tau.vec = c(0), n.strata = 4, cluster = TRUE)
> head(data)
Y S D x_1 x_2
1 1.717293 1 0 4.772092 2.4138491
2 2.553695 2 0 5.413440 2.0551019
3 2.237556 3 2 6.611161 0.9300293
4 1.825809 3 1 2.735503 1.7839981
5 5.536280 2 2 2.469239 2.0495611
6 1.628753 2 0 4.887561 2.1327071
# matched pairs (small strata)
data <- sreg.rgen(n = 100, tau.vec = c(1.2), cluster = FALSE, small.strata = TRUE, k = 2, treat.sizes = c(1, 1))
> head(data)
Y S D x_1 x_2
1 2.0393535 1 1 7.904694 1.487941
2 3.3839515 1 0 3.461776 2.832059
3 1.7250989 2 0 3.049906 3.170014
4 3.0991776 2 1 7.437064 1.098371
5 1.7406104 3 1 5.008703 1.750753
6 0.6986514 3 0 3.418835 1.375744Bugni, F. A., Canay, I. A., and Shaikh, A. M. (2018). Inference Under Covariate-Adaptive Randomization. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 113(524), 1784–1796, doi:10.1080/01621459.2017.1375934.
Bugni, F., Canay, I., Shaikh, A., and Tabord-Meehan, M. (2024+). Inference for Cluster Randomized Experiments with Non-ignorable Cluster Sizes. Forthcoming in the Journal of Political Economy: Microeconomics, doi:10.48550/arXiv.2204.08356.
Jiang, L., Linton, O. B., Tang, H., and Zhang, Y. (2023+). Improving Estimation Efficiency via Regression-Adjustment in Covariate-Adaptive Randomizations with Imperfect Compliance. Forthcoming in Review of Economics and Statistics, doi:10.48550/arXiv.2204.08356.
Bai, Y., Jiang, L., Romano, J. P., Shaikh, A. M., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Covariate adjustment in experiments with matched pairs. Journal of Econometrics, 241(1), doi:10.1016/j.jeconom.2024.105740.
Bai, Y. (2022). Optimality of Matched-Pair Designs in Randomized Controlled Trials. American Economic Review, 112(12), doi:10.1257/aer.20201856.
Bai, Y., Romano, J. P., and Shaikh, A. M. (2022). Inference in Experiments With Matched Pairs. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 117(540), doi:10.1080/01621459.2021.1883437.
Liu, J. (2024). Inference for Two-stage Experiments under Covariate-Adaptive Randomization. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2301.09016.
Cytrynbaum, M. (2024). Covariate Adjustment in Stratified Experiments. Quantitative Economics, 15(4), 971–998, doi:10.3982/QE2475